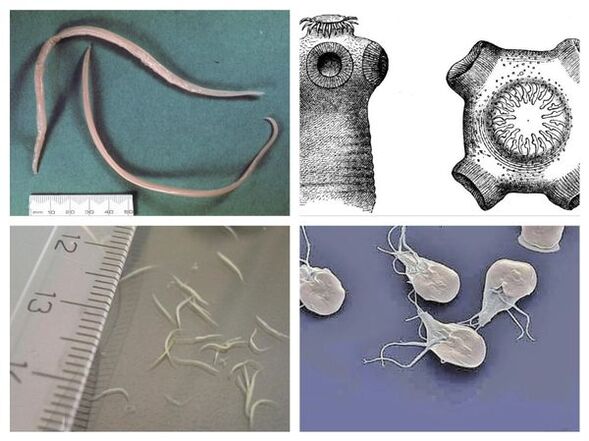
According to the World Health Organization, approximately 90% of the world's population is infected with one type of parasite or another. About 250 species of worms (helminthiasis) can live in the human body, but besides them there are also protozoa (amoebas, lamblia and others), arthropods, insect larvae and many other parasites.
Most often, residents of large cities become infected with banal worms, roundworms and tapeworms, dangerous to health and very unpleasant parasites, but only residents of tropical countries and tourists going on vacation to the South often encounter truly terrible creatures that parasitize the human body. … America, Africa or Australia.

Every day, each person is faced with a large number of parasites; you can become infected with worms by eating food or drinking water with parasite eggs or larvae, through close contact with a parasite carrier (animal or human), less often, infection occurs through household items or insect bites.
The most common parasites
- Roundworms– representatives of this type of worms are diagnosed in 100 million people worldwide every year. An adult roundworm is a roundworm, up to 40 cm long, that can exist in the human intestine for years, feeding on its red blood cells and poisoning the human body with waste. Female roundworms can lay up to 200, 000 eggs daily, which are released along with feces and infect the soil. Ascaris larvae can migrate throughout the body, affecting internal organs, blood vessels and even the human brain.
- Earthworms- small roundworms that live in the large intestine. Worm infection is common in childhood; parasites enter the human body when personal hygiene rules are not followed (not washing hands after going to the bathroom, walking and before eating, not changing underwear on time, licking fingers and so on). These roundworms do not cause poisoning as severe as other worms, but they can cause the development of diseases such as enterocolitis, vulvovaginitis, salpingitis, cystitis and others. During the breeding season, adult worms leave the lower parts of the large intestine and lay eggs in the perianal folds, which causes intense itching in the child, the main symptom of worm infection.
- Bovine and pork tapewormThese are large tapeworms, whose length can reach 10 m. Despite their impressive sizes, tapeworms are not considered the largest and longest parasites. The longest worm in the world, the broad tapeworm, can reach 25 m in length. Infection with parasites occurs when eating undercooked meat or through contact and household contact. Tapeworms not only cause intoxication and depletion of the host's body, but can also cause obstruction of the bile ducts or intestinal obstruction. No less dangerous are the larvae of worms, which penetrate the internal organs, the brain and even the eyeball.
- Giardia- protozoa or protozoan parasites that live in the small intestine of humans. Protozoal infection is possible by ingesting food or water contaminated with cysts. Diagnosing Giardia infection is quite difficult as there are no specific symptoms of the disease. A sick person constantly feels unwell, often gets sick or is diagnosed with symptoms of a variety of diseases of internal organs.
Which parasites are considered the most dangerous?
Representatives of the following species are considered the most terrible and dangerous parasites in the world: filaria, schistosomes, Guinea worms, cysticerci, toxoplasma, loa loa and some other less common parasites.
Filaria
Filariae are long, round worms, about 45 cm long; you can become infected with filarial larvae through the bite of blood-sucking insects; mosquitoes usually carry the larvae and, less frequently, other insects. Filariae penetrate the lymphatic vessels and block them. As a result of the infection, a person's lower limbs swell so much that they lose the ability to move independently.

"Elephant disease" is widespread in hot countries, affecting both local residents and tourists, and the latter in a more serious way. This disease is considered especially dangerous due to the difficulties of diagnosis and treatment - the disease becomes noticeable only when it becomes chronic, almost impossible to cure.
Schistosomes
Schistosomes are a special type of worm that live in human blood vessels. Tiny flatworms, up to 2 mm long, enter the human body when swimming or drinking water contaminated with the parasite's cercariae.
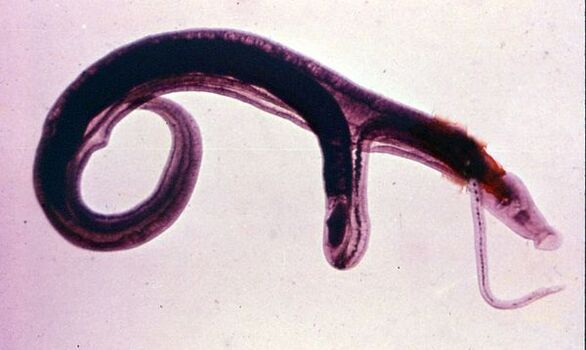
Schistosomiasis is predominantly a tropical disease, contracted by swimming in open water. Once in the human body, schistosomes can cause serious damage to the liver, bladder or intestines.
Guinea worm
Guinea worm or dracunculiasis is another serious parasitic disease that can be contracted by drinking dirty water in tropical countries. Roundworms, getting into the human intestine, literally gnaw it, then penetrate the lymphatic vessels and subcutaneous fat, where they can grow up to 80 cm in length.

Where parasites live, deep abscesses appear, inside which one or several large worms can be found. This parasite can only be cured surgically.
Loa Loa
Loa Loa or "eye worm" is a round helminth that parasitizes subcutaneous fat. A person becomes infected through the bite of a blood-sucking insect, which is the intermediate host of the parasite.
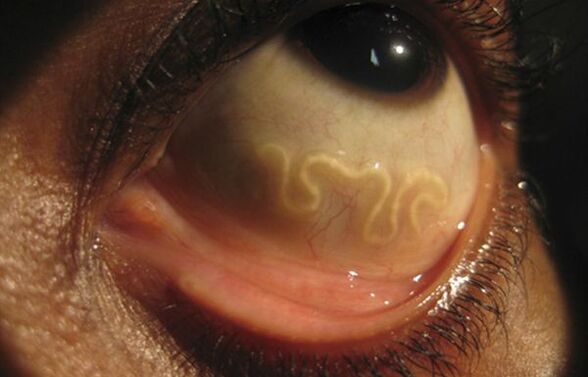
Once in the human body, Loa Loa begins to migrate throughout the body, including penetrating the eyeball, brain or nervous tissue.
Vandellia with mustache
Unlike other parasites, it belongs to freshwater fish and lives in Amazon rivers. A rather large fish - up to 15 cm long, due to its transparency and eel shape, it is almost invisible in the water and swims silently to its victims. The mustachioed vandellia can swim up to the human urethra, attach itself to the wall of a blood vessel and suck out the blood, literally eating its owner from the inside. You can only get rid of this parasite through severe surgery.
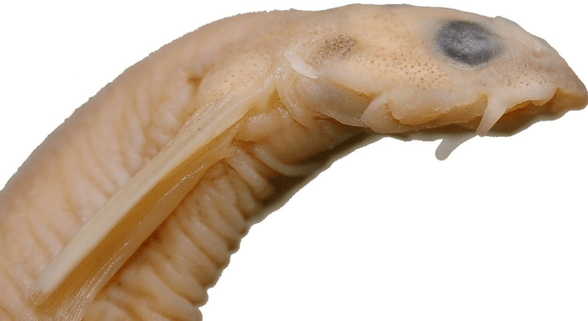
Anyone can be infected by parasites; hundreds of thousands of dangerous parasites are lurking in each of us: in the water, in the soil, on tree leaves, on public transport, in seafood, in fresh vegetables and fruits. Therefore, it is very important to follow all sanitary and hygienic standards and teach children the rules of personal hygiene as early as possible.
The entry of most parasites into the human body occurs completely unnoticed; The first symptoms of the disease appear only a few weeks or months after infection. The symptoms of parasitosis can be different: from mild malaise and headaches to a sharp deterioration in the condition, fever and hemoptysis.
Only constant monitoring of your health, regular medical examinations and extreme caution when visiting tropical countries will help you avoid infection with the most terrible parasites or, at least, diagnose such an infection in time.